Alcohol use disorders
The word “Alcoholism” should be cautiously used, it refers to damage whether mental, physical or social, resulting from excessive consumption of Alcohol.
What makes a person to take alcohol? Or why people drink alcohol?
The reasons for substance use are varied, often mixed. They include
- A search for a “High”
- A search for a repeat of initial pleasurable effects
- Cultural norms in some sub-cultures
- Self medication for anxiety, social phobia, insomnia etc
- Self medication for chronic painful conditions
- As a consequence of mood elevation in mania
- To overcome withdrawal symptoms, like hand tremors, insomnia, gastric upset
- To yield for craving to alcohol
- To get energy or courage in facing stressful situations like conflicts with neighbors, or within marital relationship
Consequence of alcohol intake
Acute alcohol consumption beyond ones normal capacity can lead to loss of judgment and serious social disruption or physical hazard is known as Acute Intoxication
This can lead to inappropriate behavior, impaired judgment, hypersexual or aggressive behavior
- Acute Intoxication can cause acute gastritis, esophageal tear
- Poor judgment (e.g. Jumping from height due to believing one can fly)
- toxic effects of contaminants in illicit liquor- methanol poisoning- death & blindness
- Road traffic accident
- secondary medical problems
- secondary psychiatric problems
- risk of development of dependency
- Negative social, occupational, marital, and forensic consequences
Types of alcohol users
- Social drinker: who takes on social occasions such as marriage functions
- Harmful use/ abuse pattern: though the person drinks alcohol on an occasion but in large gulps leading to intoxication behavior
- Binge drinking: refers to drinking for extended period of time (2-7days) where he is intoxicated during these periods and remains abstinent for 15-30 days. Once they start they can’t stop, and stop till all their money exhausted or when they can no more drink due to gastritis.
4.Dependence pattern
Symptoms of Alcohol abuse/ alcohol harmful use
- Recurrent excess of alcohol intake leading to impairment in social or occupational functioning
- Frequent Legal problems whenever alcohol is consumed
- Hazardous drinking like drunken driving, sexual harassment etc.
- One of the major obligations is missed like work or school or home
A 36 year old IT professional from a reputed MNC company, brought by his wife complaints of his alcohol intake every month end, where he drinks in excess during the month end parties. In the last one year there were many occasions where had had one or other problem following his uncontrolled alcohol intake, once he was arrested for drunken driving, another occasion he had tried to molest a female colleague, another month he developed acute gastritis and was hospitalized for a week, last week he had a fall in the stairs and fractured his arm.
In between periods he is a sincere hard worker
Alcohol Dependence
A person is said to be dependent (addict) to alcohol when he has the following characters
Tolerance
After taking substance for long period of time the person needs increasing amount of the substance to get the desired effect.
Example a person taking 2 pegs of alcohol for the last 2months would feel not getting the “kick” for the 2 would get it only after 3 pegs and so on.
Withdrawal
After a regular intake of alcohol over months the person attempts to reduce the quantity or stops suddenly he gets specific withdrawal manifestations which make him to take alcohol, thus he needs alcohol for his daily living.
Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal are
- Increased pulse rate > 100/min
- Sweating
- Hand tremors (observed when asked to extend his hand with fingers stretched apart)
- Insomnia
- Nausea and vomiting
- Anxiety (panic attacks)
- Psychomotor agitation
- Transient visual or auditory hallucinations
- Seizures
- Repeated attempts to cut down
- Increasing amounts of alcohol over period of years
- Significant time is spent on purchasing and taking alcohol letting aside social or occupational obligations.
- This pattern of alcohol intake has caused significant social-occupational impairment
- Due to prolonged alcohol intake there is diagnosable medical illness like gastritis, hepatitis, and the person continues to consume alcohol even if he is made aware of his illness
A 45 year old married man, with two children, working as 2 wheeler mechanic and brought by his wife with complaints of hand tremors, sleep disturbances, and intense craving to take alcohol
Patient accepted to have started his alcohol habit when he was a boy 15 years when his owner used to consume alcohol, he initially started to take the left out from the wine bottle, over period of years he started buying every day evening after routine work.
10 years ago he got married and abstained from this habit for about 6 months; gradually he started consuming on Saturday’s and later weekly twice, thrice and now every day.
His wife objected when he stared taking in noon hours and nowadays he takes in morning at 8 AM as soon as he wakes up.
Over the last six months he is highly irregular to work, and whatever he earns he spends on alcohol and hardly cares wife or children. His wife is forced to work in a sweet shop to support the family which again he does not like her working, rather suspects her character and physically abuse her.
Last month he had a bout of blood vomiting and was reported by doctor he had gastric ulcer he was admitted for a week and soon started to consume on the subsequent week.
Diagnosis
The CAGE questionnaire: simple bed side assessment of alcohol dependence
- Cut down-ask patient whether he feels that he is taking alcohol in excess and had ever thought of reducing alcohol or attempted to stop it.
- Annoyed-ask whether he frequently gets annoyed at people (family members) who question about his alcohol intake.
- Guilt feeling –ask whether he has ever felt guilty due to persistent alcohol consumption
- Eye opener-ask if he has the urge to take alcohol immediately after waking up.
Rating scales to find the severity of alcohol intake
These are free downloadable questionnaire to diagnose alcohol dependence and its severity
Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT)
Severity of Alcohol Dependence Questionnaire(SADQ)
Alcohol Problems Questionnaire
Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment of Alcohol Scale, Revised (CIWA-Ar)
Etiology
Why people become Alcohol dependent, while some take only on occasions?
- Alcoholism runs in family, if a person dependent on alcohol there is 25% chance that his son in future will become dependent.
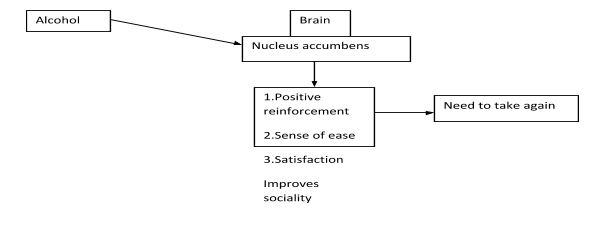
- Alcohol acts as positive reinforcement, hence if a person under stress consumes alcohol once it act as reliving factor, which drives him to take whenever he has stress, this continues and the person takes every day claiming he had stressful day work.
- Alcohols relieve insomnia, social anxiety, depression, pain; but temporarily hence he may use it to overcome, and in due course he has to take every day.
- As a part of social custom to drink during occasions like new year eve, or festivals and gradually the frequency of occasions increases
To overcome the trouble within the family example: conflict with mother and spouse
As a part of management of his daily stress , saying he has been overworked, or to sleep well to work for next day
Psychological defences used by an Alcoholic
Denial- I am not addict.
Rationalization- all are drinking. Why can`t I. It is for relaxation. I am in full control.
Projection – I was normal only only because of wife`s torture and Boss`s ill-treatment I was forced to take alcohol.
Liver dysfunction
Liver is the main organ to metabolize alcohol, thus when a person is consuming alcohol every day over months and years; because of the gastritis, poor food intake, poor absorption, essential vitamin deficiency and protein malnutrition, liver is affected gradually over time.
The liver is burdened to digest alcohol and to produce the needed nutrients, gradually fat gets accumulated in the liver cells – which is seen in USG scan as Hepatomegaly “FATTY LIVER”
As the consumption continues, liver is no longer capable to hold and the cells starts dying, the toxic chemicals are released, liver is not able to digest the food, purify blood; Bilirubin is released and the person develops Jaundice and other clinical symptoms of “HEPATITIS”.
Alcoholic hepatitis is a progressive inflammatory liver injury due to decades of alcohol consumption.
Person stops alcohol for a short period* and then continues again, now the liver can’t bear any more starts shrinking leading to nodular formulation, tiny bubbles of 1mm nodules form all over the liver this is called as “HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS” this leads to a irreversible damage of liver and the liver no longer does its function.
Indigestion, loss of appetite, weight loss, jaundice, blood vomiting (Hematemesis ) collection of fluid in abdomen (ascites), bilateral swelling of legs (pedal edema),altered sleep cycle and confusion sets in known as “HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY”
These patients may develop electrolyte imbalance, thrombocytopenia, hematemesis and hypoalbuminemia ,portal hypertension and mortality rate is high
Some survivors may soon develop “HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA”
*if the person stops alcohol at this stage his liver can be saved
B-complex deficiency
The person with alcohol dependence are poor eaters, or digest poorly thus leading to poor nutrition and deficiency of B complex vitamins like B1, B6, B12. These deficiencies affect Brain and Peripheral nerves leading to parastheisa in legs (tingling sensation in legs, loss of sensation in feet), cramps in limbs, memory disturbances.
A triad of Confusion, Ophthalmoplegia( eye disturbances), Ataxia (gait disturbances) is called as “Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (WKS)”
The patient may have disturbances in recent memory and add up stories to their loss known as “Confabulation”. This is due to Vitamin B1 deficiency essential in brain metabolism
Socio occupational consequences
- Marital disharmony
- Conflicts at work place
- Conflicts with neighborhood
- Increasing debts
- Legal problems-e.g. for drunken driving
- Stigma as “alcoholic” in the society
- Depression
- Suicide
- Anxiety disorders like Panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, GAD
- Sexual dysfunction (Erectile dysfunction)
- Sleep disorder
- Psychotic disorders with delusions: Delusion of infidelity (Morbid Jealousy) is commonly found in alcohol where he constantly suspects his wife and harasses her.
- Psychosis with hallucinations
8. Delirium: this is called as “Delirium Tremens” –typically occurs on the third day of withdrawal, the patient is markedly agitated, disoriented, erratic sleep pattern, hallucinations and seizures called “Rum fits”.
The hallucination typically consists of birds, animals, insects crawling or tiny people called “Lilliputian hallucinations”.
The condition is indicative of an underlying physical complications due to alcohol and if untreated increases mortality.
9. Dementia: alcohol dependence can drive a person to early dementia
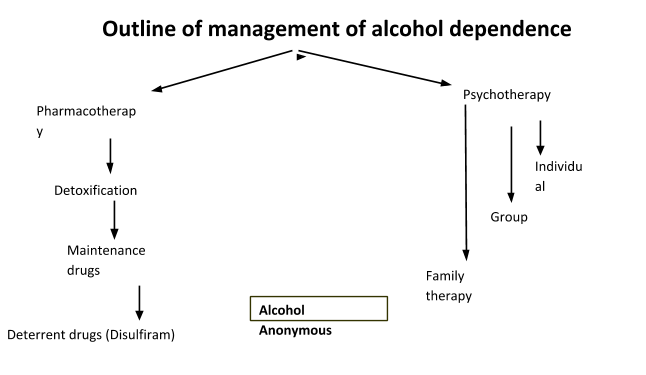
- Benzodiazepines like Lorazepam-10-12mg per day to start with and reduced one tablet a day after 5 or 6 days.
- B complex vitamins esp. B1 , B6, B12 usually given in injectable forms initially then oral forms
- IV fluids and electrolyte correction
- Antibiotics, liver supplements, proton pump inhibitor- Pantoprazole
- Managing co morbid medical conditions- diabetes, cardiac problems etc
Once the withdrawal symptoms are reduced patient is assessed for motivation to quit, ideally he is referred to a De-addiction centre for psychotherapy.
In a de-addiction centre 4 weeks of inpatient therapy is given
Explored for the history of alcohol intake once again, patient is made to verbalize how he started to drink and how he reached the current dependence level
He is allowed to acknowledge the extent of social-occupational-financial difficulties following his alcohol dependence
He is highlighted about the medical or neurological complications he has developed
He is educated about the comorbid psychiatric condition and appropriate medications started for it
Other forms of rehabilitation – Yoga, Gym exercise, Art therapy, Group therapy, and motivational videos are provided.
His spouse or other family members are called in, psychoeducated, and ongoing interpersonal problems, financial constraints are sought out
Family members are educated how to handle him during his sober free life
Certain drugs are prescribed that have evidence to prevent craving, reduce binge intake of alcohol
- Naltrexone(50-150mg),
- Acamproaste(333mg QDS),
- Topiramate(100-200mg)
Deterrent drugs ; Disulfiram– the drug when taken along with alcohol acts adversely by blocking acetaldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme which leads to accumulation of acetaldehyde in blood leading to toxic reactions such as flushing, increased heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate and may lead to cardiac arrest.
The patients are warned about this reaction and consent is taken before prescribing.
Due to the fear the person remains abstinent but until he takes the drug
Following discharge patient is referred to AA group
Alcohol Anonymous (AA)
This is a self help group formed by ex-alcoholics in a motto to help others who are suffering from alcohol related disorders. There is a weekly meeting where they share their ideas and educate the fellow consumers. A similar group meeting for spouses called “Al-Anon” and “Al-Ateen” for teenage children. But the latter two are not widely found in India.